How Cities are Shaping the Future of Apprenticeships – Insights from the EU and US webinar
15/10/2024

On Monday 14 October 2024, EARLALL co-organised together with the Metropolitan City of Rome the webinar “The Role of Cities in Fostering Apprenticeships – Best Practices Between the EU and the US” in the framework of the European Alliance for Apprenticeships Community on the Role of Cities and Regions in fostering apprenticeship, leady by the two organisations, and the Fundación Bertelsmann. The webinar brought together city leaders and apprenticeship experts from the European Union and the United States to discuss cities’ pivotal role in fostering apprenticeships. Key participants included representatives from the European Commission, the city of Rome, and Tacoma, Washington.
The event started with Anna Barbieri of the European Commission, who acknowledged the importance of including voices from outside the EU to enrich the discussion. The meeting had participants from both sides of the Atlantic. She emphasized that apprenticeships play a crucial role in linking education to employment, fostering collaboration between schools, training centres, and businesses.
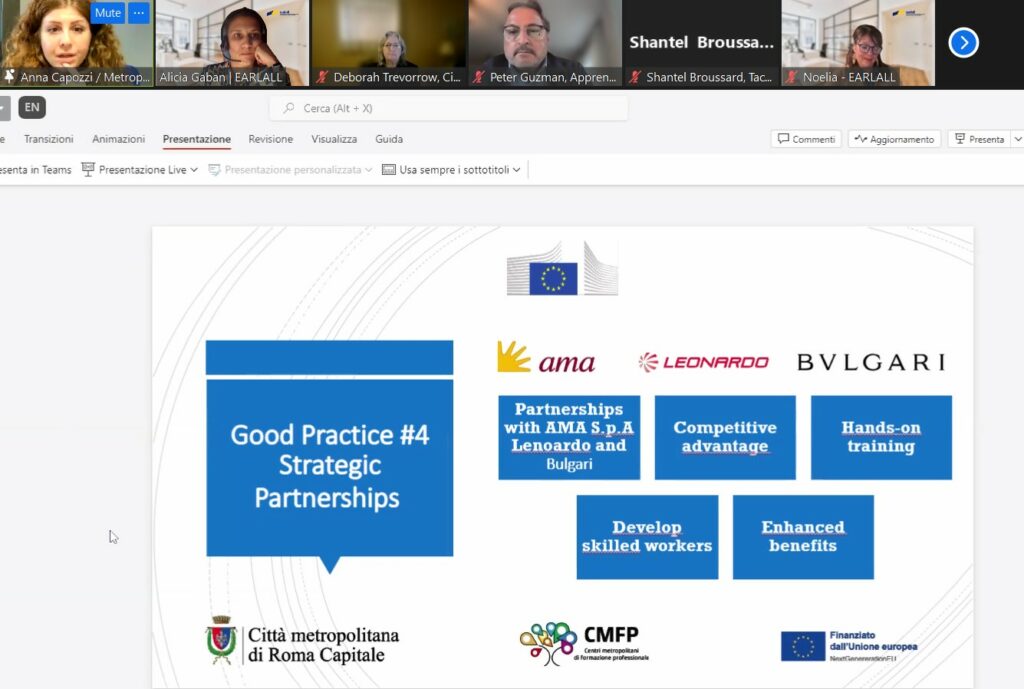
Rome’s Deputy Mayor, Daniele Barucci, shared insights into how the Italian capital has tackled high dropout rates by promoting vocational education. Apprenticeships have been a key strategy in ensuring that students stay in school while gaining practical skills, supported by partnerships with large companies like ama, Leonardo and BVLGARI.
One of the standout examples came from Tacoma, Washington, where Mayor Victoria Woodards presented the city’s Leap (Local Employment and Apprenticeship Program). Established in the late 1990s, Leap was designed to address high unemployment rates and ensure that residents, particularly those from economically distressed areas, could access training and employment through apprenticeships.
Tacoma’s Leap Program: A Success Story from the U.S.
Deborah Trevorrow, a representative from Tacoma’s Leap Advisory Committee, provided a detailed breakdown of the program’s compliance measures. She shared data demonstrating significant improvements in both participation and outcomes, with increased adherence to apprenticeship hour requirements. Leap mandates that 15% of labor hours on public projects must be performed by local residents, and an additional 15% by registered apprentices. The program also enforces penalties for non-compliance, creating accountability among employers. Leap has been a resounding success, helping to bolster local employment while ensuring high-quality apprentice training.
Peter Guzman from the State Apprenticeship and Training Council in Washington discussed how the state regulates apprenticeships to ensure both quality and inclusivity. He touched on the dual role of the Department of Labor in providing oversight and ensuring that apprenticeships align with trade-specific requirements, ultimately benefiting both employers and apprentices. Further information on the Washington State Apprenticeship and Training Council (WSATC) is available here.
Shantel Broussard, from Tacoma Water, shared another local success story. Tacoma Water has 300 employees, half of whom began their careers as apprentices through the utility’s water worker apprenticeship program. The program is extensive, involving over 3,000 hours of training and multiple progression steps that allow workers to build their careers in the utility sector. To support the pipeline of talent, Tacoma Water partners with schools for job shadowing and career tours, and engages in community outreach through events like the Women in Trades expo. Shantel also highlighted the Tacoma Training and Employment Program (TTEP), which offers temporary job placements for graduates of pre-apprenticeship programs, breaking down barriers and promoting diversity within the industry.
Rome’s Approach: Bridging Apprenticeships with Education
On the other side of the Atlantic, Anna Capozzi from the Metropolitan City of Rome discussed how Rome’s vocational training institutions support students between 14 and 17 years of age, giving them hands-on experience before they enter the workforce. The city has forged strong partnerships with major companies and is now working on expanding collaborations with local artisans to create more apprenticeship opportunities in the arts and crafts sectors.
Lessons and Future Collaboration
Peter Guzman noted the possibility of creating a portable apprenticeship credential that could be recognized across both the U.S. and Europe, which would open up new opportunities for workers in a globalized economy.
This webinar highlighted how cities, with the right strategies, can play a transformative role in fostering apprenticeships. By fostering partnerships, leveraging data for compliance, and creating inclusive programs, cities like Tacoma and Rome have become models for effective apprenticeship systems. The discussion underscored the importance of tailoring apprenticeship programs to meet the specific needs of local communities, providing a roadmap for other cities looking to bolster their vocational training systems.
Resources




